Understanding indirect ophthalmoscopes for retinal examination
Shedding light on Scan Optics’ innovative indirect ophthalmoscope
To detect and evaluate symptoms of retinal detachment or eye diseases such as glaucoma, ophthalmoscopy may also be performed if you have signs or symptoms of high blood pressure, diabetes, or other conditions that affect the blood vessels.
The working principle of an indirect ophthalmoscope
The indirect ophthalmoscope works with the principle of converging optics. The condensing lens is positioned between the patient’s eye and the examiner, projecting an inverted and magnified image of the retina onto the examiner’s retina. The binocular eyepieces provide a stereoscopic view, allowing for depth perception and a comprehensive assessment of retinal structures.
The light source within the headset illuminates the retina, passing through a small aperture in the condensing lens. This focused light lets the examiner visualise intricate retinal details, including the optic nerve, blood vessels, and peripheral regions. By adjusting the lens and eyepieces, the examiner can navigate different areas of the retina to detect abnormalities or pathologies.
A brief introduction to Scan optics Indirect ophthalmoscope
Scan Optics Indirect Ophthalmoscopes are an important device for ophthalmologists and optometrists, offering advanced illumination for clear retinal imaging and an ergonomic design for versatile, easy use in various clinical settings. Designed to offer a wide field of view, adjustable comfort, and advanced illumination, both lightweight instruments are the perfect tool for retinal examination.
The Scan Optics head mount indirect ophthalmoscope combines precision, comfort, and versatility in one advanced instrument. Designed for eye care professionals who require reliable tools for comprehensive retinal examinations, this ophthalmoscope features an ergonomic design for prolonged use and an adjustable head mount for a tailored fit.
With its high-intensity LED illumination and advanced optical unit, our indirect ophthalmoscope delivers clear, bright retinal images essential for accurate diagnosis and patient care. Interchangeable filters and an optional teaching mirror make this instrument adaptable for both clinical practice and educational purposes.
Watch the Scan Optics head mount indirect ophthalmoscope in action
Learn how its innovative features provide ease and accuracy during eye examinations.
Highlights
Ergonomic design
Lightweight and comfortable for extended use
Customisable fit
Easily adjustable head mount for personalised comfort
Advanced illumination
High-intensity LED light source with adjustable setting.
Versatile use
Suitable for a variety of clinical and educational applications
Understanding Indirect ophthalmoscopes and insights into Scan Optics’ Indirect ophthalmoscope
Indirect ophthalmoscopes are essential instruments for optometrists and ophthalmologists, enabling to detect and evaluate symptoms of retinal detachment or eye diseases such as glaucoma comprehensive retinal examinations and accurate diagnoses. They provide a wider field of view and a stereoscopic image of the retina. This capability is crucial for diagnosing conditions like diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment, and age-related macular degeneration.
As an Australian manufacturer of ophthalmic surgical microscopes, we have developed two models of indirect ophthalmoscopes SO-2200-spectacle mount and SO-2700-lightweight head mount. Both designed to meet the diverse needs of eye care professionals.
The Scan Optics Indirect Ophthalmoscopes combine precision, comfort, and versatility in one advanced instrument. Designed for eye care professionals who require reliable tools for comprehensive retinal examinations, this ophthalmoscope features an ergonomic design for prolonged use and an adjustable head mount for a tailored fit.
With its high-intensity LED illumination and advanced optical unit, our indirect ophthalmoscopes deliver clear, bright retinal images essential for accurate diagnosis and patient care. Interchangeable filters and an optional teaching mirror make this instrument adaptable for both clinical practice and educational purposes. Available in various sizes and colours, it meets the diverse needs of professionals seeking a balance of performance and comfort in their practice.
Key features of indirect ophthalmoscopes
Wide field of view
Offers a panoramic view of the retina, including the periphery, essential for detecting subtle abnormalities.
Stereoscopic imaging
Provides stereoscopic view of the retina, aiding in the accurate assessment of retinal depth and topography.
Adaptable for various positions
Suitable for examining patients in different positions, including supine, sitting, or standing, enhancing versatility in clinical settings.
Bright Illumination
Utilises a focused light source to illuminate the retina clearly, improving visibility of structures like the optic nerve and blood vessels.
Key components of an Indirect ophthalmoscope
An indirect ophthalmoscope consists of several key components that work together to provide a detailed view of the retina:
Condensing lens
A +20 diopter convex lens projects an inverted, magnified image of the retina. – The lens is not included.
Binocular eyepieces
Allow the examiner to observe the retina providing a stereoscopic view in three dimensions.
Light source
Typically, an LED is located within the headset to illuminate the retina through the condensing lens.
Adjustable head mount
Ensures a secure and comfortable fit for the examiner, allowing for precise positioning of the optical unit.
Indications for using an indirect ophthalmoscope
Indirect ophthalmoscopes are used in various clinical situations where a comprehensive view of the retina is crucial. They are particularly valuable for diagnosing, monitoring, and managing a range of ocular conditions.
Common clinical indications
Comprehensive retinal examination
Used for detailed assessment of the retina to detect conditions like diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment, and age-related macular degeneration.
Routine eye exams
Assists in evaluating the overall health of the retina and optic nerve, even in patients without specific ocular complaints.
Diagnostic and monitoring applications
The indirect ophthalmoscope plays a crucial role in both diagnosing ocular conditions and monitoring disease progression. For instance, it is used to track changes in conditions like diabetic retinopathy or glaucoma, allowing eye care professionals to adjust treatment plans as needed.
Emergency eye care
Essential for assessing acute retinal conditions such as retinal tears, detachment, or trauma.
Paediatric eye care
Advantages of using an indirect ophthalmoscope
Key advantages of using an indirect ophthalmoscope
Indirect ophthalmoscopes offer a range of advantages that make them an essential tool for comprehensive retinal examination.
Wide field of view
Offers a panoramic view of the retina, including peripheral regions, which is crucial for detecting conditions such as retinal detachment and diabetic retinopathy.
Versatility
Suitable for examining patients of all ages and adaptable to various positions (supine, sitting, standing), enhancing its use in different clinical scenarios.
Comfortable working distance
Allows the ophthalmologist to maintain a comfortable distance from the patient, making it easier to examine patients with small pupils or media opacities.
Bright illumination
Equipped with a bright, focused light source to clearly visualise retinal details like the optic nerve and blood vessels.
Enhanced diagnostic capabilities
By offering a comprehensive view of the retina and providing depth perception, indirect ophthalmoscopes significantly enhance diagnostic capabilities. They allow healthcare professionals to detect subtle retinal changes and monitor more effectively.
Versatility in clinical practice
One of the primary advantages of the indirect ophthalmoscope is its ability to provide a wide and panoramic view of the retina. Unlike the direct ophthalmoscope, which offers a limited field of view, the indirect ophthalmoscope allows the examiner to observe a larger area of the eye’s interior, including the peripheral regions.
Use in routine eye examinations
During routine eye exams, the indirect ophthalmoscope is used to assess the overall health of the retina and optic nerve. Its ability to provide a detailed view allows for the early detection of subtle changes or abnormalities, facilitating timely intervention and management.
Role in surgical and emergency settings
In surgical settings, the indirect ophthalmoscope assists ophthalmic surgeons in procedures that require detailed retinal visualisation. In emergency settings, it is used to quickly assess retinal conditions that may require immediate attention, such as retinal detachment or trauma-related injuries.
Key features to consider when choosing an indirect ophthalmoscope
Choosing the right indirect ophthalmoscope is crucial for achieving accurate and effective retinal examinations. Here are the key features to consider when selecting an ophthalmoscope that best suits your clinical needs.
Illumination quality and intensity
LED light source
Look for an ophthalmoscope with an LED light source for bright, consistent illumination that enhances retinal visibility.
Adjustable intensity
Choose a model with adjustable light intensity to adapt to different examination conditions and patient comfort.
Ergonomic design and comfort
Lightweight construction
A lightweight design minimizes strain during long clinical sessions.
Adjustable head mount
An adjustable head mount ensures a secure and comfortable fit, reducing fatigue for the examiner.
Optical quality and field of view
High-resolution optics
Opt for an ophthalmoscope with high-resolution optics that provide clear and detailed views of the retina.
Wide field of view
A wide field of view allows for comprehensive retinal examinations, including the peripheral retina.
Versatility and adaptability
Interchangeable filters
Consider models with interchangeable filters, such as cobalt and red-free filters, for enhanced examination flexibility.
Portability
For those conducting fieldwork or domiciliary visits, a portable design with a compact carrying case is beneficial.
Optimised solutions for every eye care professional
Explore how Scan Optics can support your practice or service. Find out how we can help you achieve the highest standards of care.
Scan optics models and innovations in indirect ophthalmoscopy
Transition to Scan Optics' offerings
Among the various types of indirect ophthalmoscopes, Scan Optics offers advanced binocular models that stand out for their innovative features and ergonomic design.
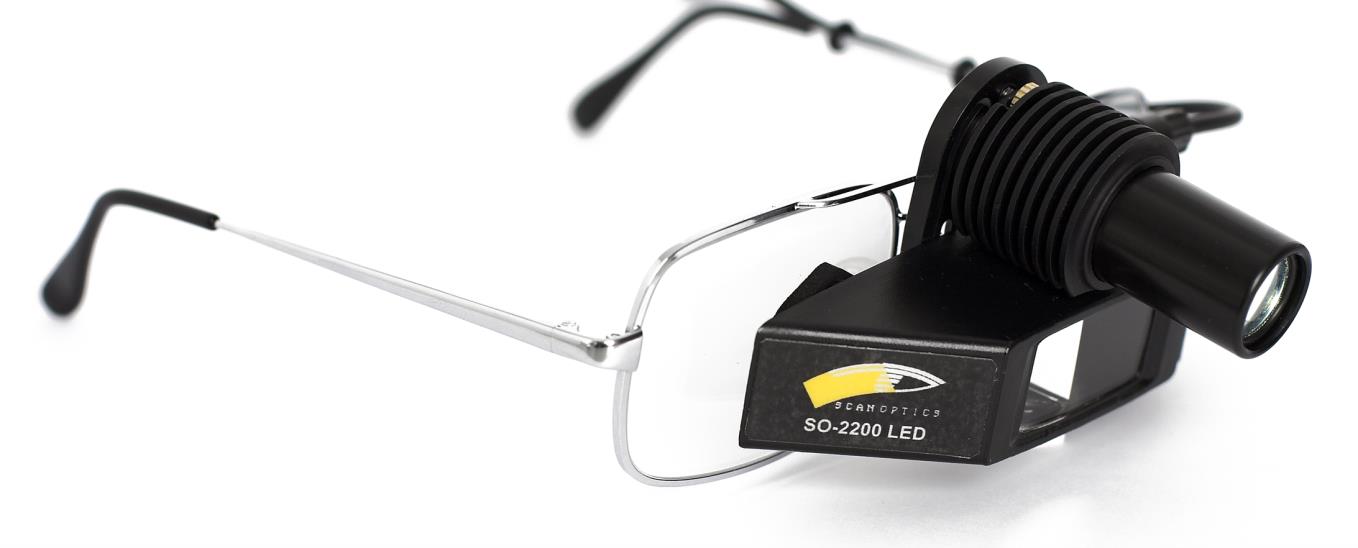

Scan Optics SO-2200 LED binocular indirect ophthalmoscope
Advanced LED illumination
Equipped with a high-intensity LED lamp that delivers bright, consistent illumination for clear retinal imaging.
Customisable fit
Features an adjustable head mount and ergonomic design, ensuring comfort during prolonged use.
Lightweight construction
Designed to minimise strain on the examiner, enhancing ease of use.
Interchangeable filters
Comes with cobalt and red-free filters to suit various examination needs.
Portable and convenient
Includes a compact carrying case, making it ideal for use in different clinical environments.
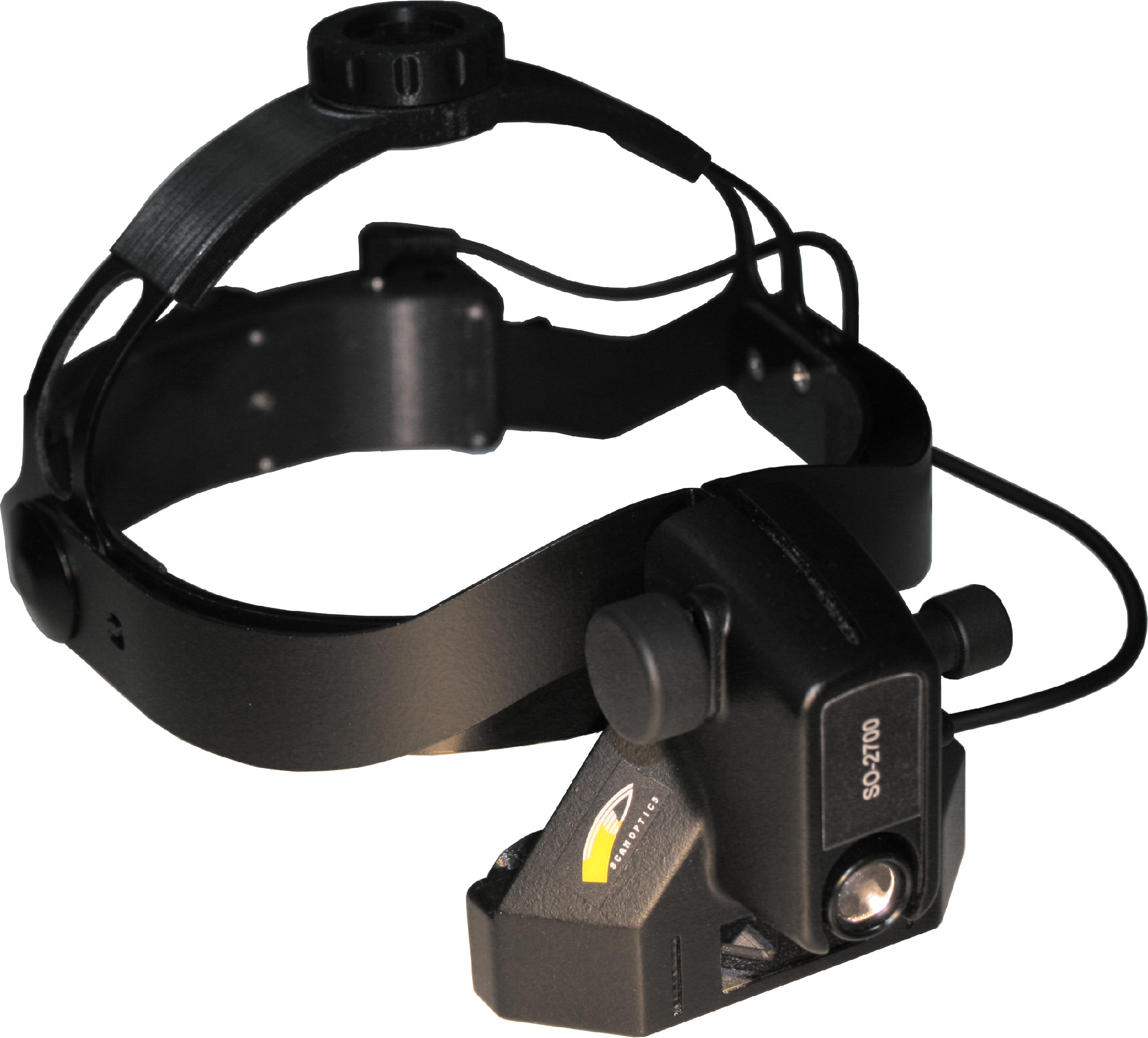

Scan Optics SO-2700 head mount wireless binocular indirect ophthalmoscope
Wireless design
Features a small, integrated battery pack, allowing for unrestricted movement and convenience during examinations.
Precision optics
Offers high-resolution, undistorted three-dimensional views of the retina, essential for accurate diagnosis and patient management.
Adjustable head mount
Provides a secure, customized fit with adjustable bands to reduce strain during extended use.
Enhanced portability
Ideal for fieldwork and domiciliary visits, ensuring comprehensive eye exams regardless of location.
Portable and convenient
Includes a compact carrying case, making it ideal for use in different clinical environments.
Step-by-step guide on using Scan Optics indirect ophthalmoscope
Using an indirect ophthalmoscope effectively requires precision and skill. This step-by-step guide provides a systematic approach to help eye care professionals conduct a thorough and accurate retinal examination.
1. Prepare the patient
Explain the procedure to the patient to ensure their comfort and cooperation. Dim the room lighting to enhance retinal visibility.
2. Position the patient
Have the patient sit or lie down comfortably, ensuring their head is aligned and supported.
3. Adjust the ophthalmoscope
Put on the indirect ophthalmoscope headset and adjust it for a secure, comfortable fit. Turn on the light source and set the brightness to an appropriate level.
4. Insert the condensing Lens
Hold the +20 diopter lens approximately 2-3 inches from the patient’s eye, centring it to capture a clear image. It does not come with the lens.
5. Focus and observe
Look through the binocular eyepieces, adjusting the focus until you achieve a clear view of the retina. Begin by examining the optic nerve head and move systematically across the retinal surface.
6. Adjust the view
Manipulate the lens and the light source to explore different areas of the retina, including the periphery, macula, and optic nerve.
7. Document findings
Record observations, noting any abnormalities or areas of concern for comprehensive patient documentation and follow-up care.
8. Optimise light intensity
Adjust the light source to avoid discomfort for the patient while ensuring sufficient illumination for a detailed view.
Maintenance and care of Scan Optics indirect ophthalmoscopes
Proper maintenance and care are vital to ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of Scan Optics indirect ophthalmoscopes. These instruments, designed for durability, can be relied upon for consistent performance. Regular cleaning and inspections are essential to keep them functioning at their best, but their robust construction provides peace of mind.
Maintenance guidelines
To maintain your Scan Optics indirect ophthalmoscope, start with regular cleaning using a soft, lint-free cloth and a mild, approved disinfectant solution. Gently wipe down the lenses and headset after each use to prevent the spread of infections and ensure that the lenses remain clear for unobstructed views. The lenses in Scan Optics models are sealed from dust, reducing the need for frequent cleaning and lowering the risk of internal damage.
Scan Optics’ LED light sources are designed to last the instrument’s lifetime, minimizing the need for replacements. Periodically check the brightness and performance of the light to ensure it meets clinical needs. Interchangeable filters and attachments, available with Scan Optics models, should be handled with care and stored in their designated compartments to avoid scratches or damage.
Store your Scan Optics ophthalmoscope in the provided carrying case to protect it from dust and potential damage when not in use. These cases are designed for secure storage and easy transport. Regular inspections for signs of wear are not just recommended, but a responsibility, even though Scan Optics instruments are built for durability. This proactive approach to maintenance ensures that your Scan Optics ophthalmoscope continues to deliver high-quality retinal examinations.
